Licensing requirements
In New York, there is no official HVAC license requirement at the state level. However, some local municipalities have their own licensing requirements. For example, Buffalo has a licensing procedure for working as a heating contractor, including submitting references, a work history, and passing an exam. In Ithaca, HVAC contractors must obtain a certificate of registration. Syracuse requires a license with specific education and experience, along with an exam. New York City has three different types of licensing for HVAC professionals.
HVAC certifications
There are several types of nationwide certifications available for HVAC professionals, including:

NATE Certification
The North American Technician Excellence (NATE) certification is nationally recognized and is based on an exam. It is not required, but highly recommended for HVAC and refrigeration technicians. NATE certified technicians typically earn more than their non-certified peers and remain in the industry for longer.
That being said, if the business you’re considering to be is more of an exclusive partner (a tech you’d like to use as a competitive advantage, for example), then you should also make sure your clients can make good use of what that potential partner has to offer. You don’t want to fancy yourself with a brand-new purchase only to discover there is no demand or use for it. If you’re unsure about the industry you’re dealing with or the product you’re looking into, don’t hesitate to consult an expert.

EPA 608 Certification
The federal government requires technicians to obtain EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) certification if they handle units that contain refrigerant:
- Type I Certification – for the repair and installation of small appliances like vending machines, domestic refrigerators, and window AC units
- Type II Certification – for the repair, installation, and disposal of equipment and appliances that contain high-pressure refrigerants, like residential AC units, heat pumps, process refrigeration, and commercial refrigeration
- Type III Certification – for the repair, installation, and disposal of equipment and appliances that contain low-pressure refrigerant usually found in industrial equipment
- Universal Certification – for the repair, installation, and disposal of equipment of all kinds, no matter the refrigerant type

HVAC Excellence Certification
HVAC Excellence Certification focuses on experience gained by HVAC professionals over time.
- Professional Level HVAC Excellence Certification requires at least 2 years of experience and a successful score in a comprehensive exam on specialty subjects such as ventilation services and residential heat pumps.
- Master Specialist Level HVAC Excellence Certification requires at least 3 years of experience in addition to already having Professional Level Certification.

HVAC licenses in different parts of New York
Buffalo
HVAC licensing is overseen by the City of Buffalo Division of Fuel Devices. The Buffalo HVAC exam fee is $50.
Buffalo has several classes of licenses for heating contractors:
- Class IA (Chief Engineer, $125) and Class I (IB, $100) cover the service and installation of equipment that uses specific kinds of gas, fuel oil, or solid fuel.
- Class II ($75) allows the service and installation of equipment that uses gas or solid fuel.
- Class III ($50) permits the service and installation of stoves, fireplaces, prefabricated fireplaces, and solid fuel add-ons.
In Ithaca, heating and/or ventilation engineers, contractors, or installers must apply for a certificate of registration that is renewed annually ($50) and can be obtained in the Building Department.
Syracuse
HVAC licensing is overseen by the Division of Code Enforcement in City Hall Commons and includes several classes:
- Class A ($200) – Master HVAC Mechanical License, requires 10 years of work experience
- Class B ($100) – Limited HVAC Mechanical License, requires 5 years of work experience
- Class C ($100) – Residential HVAC Mechanical License, requires 5 years of work experience
- Class M ($100) – Master Refrigeration Mechanical License, requires 5 years of experience
- Class R ($75) – Limited Refrigeration Mechanical License, requires 5 years of experience
- Class R ($75) – Limited Refrigeration Mechanical License, requires 5 years of experience
- Class V – Special Mechanical License
HVAC license applicants in Syracuse must pass an exam given by the licensing board. Syracuse maintains an online record of local licensed HVAC contractors.
New York City
There are several types of certifications available for HVAC contractors in New York City, each with its own application process and set of fees:
Oil Burning Equipment Installer
- Exam application fee ($525)
- Practical exam ($350)
- Background check ($500)
- License issuance fee ($100)
- Seal fee ($100)
- Renewal fee ($150 every 3 years)
Class A requires 4 years of experience / Class B requires 3 years of experience.
High-Pressure Boiler Operating Engineer
- Exam application fee ($525)
- Practical exam ($350)
- Background check ($500)
- License issuance fee ($100)
- Renewal fee ($50)
Refrigeration Operation Engineer
This certification is overseen by the FDNY and covers many types of air conditioning systems.
- Written exam ($60)
- Practical exam ($225)
- Certificate of Fitness fee ($25)
- Fee waivers may apply for government employees

Advantages of an HVAC license
Even if you don’t live in one of the New York State municipalities that requires HVAC licensing, there are still several reasons you may choose to get licensed:
- Learn valuable industry skills you can immediately apply on the job
- Reassure customers of your professional abilities, earning you more and higher-paying jobs
- Gain the ability to work in other areas that do require a license
- Increase your salary expectations
- Further establish yourself in your career as an HVAC professional
Becoming an HVAC professional in New York
Here are the steps to follow on your HVAC career path:
- Have your high school diploma or GED
- Be at least 18 years of age
- Choose a training program. You can attend a trade school, technical college, or community college to learn the material and prepare for your certification exams.
- Become an entry-level worker through employer sponsorship or be an apprentice through a union or trade organization.
- Obtain licensing and certification for skills like handling refrigerant, gas fitting, and warm air ventilation. Additional certifications will improve your salary and marketability.
- Set up insurance based on your needs. While New York does not require HVAC professionals to have a minimum amount of insurance, an HVAC company must have unemployment insurance and worker’s compensation. Some areas, like New York City, may have their own insurance requirements. If you run your own HVAC business, professional liability insurance can cover you in case of injury or property damage.

Capital Region Career Technical School, Albany, NY.
HVAC schools and training programs in New York
Ready to start your career as an HVAC professional? Contact a training program at one of the following colleges or institutes:
- Alfred State College, Wellsville, NY (607) 587-4133
- Apex Technical School, New York, NY (212) 645-3300
- Branford Hall Career Institute, Bohemia, NY (631) 589-1222
- Broome-Tioga BOCES, Binghamton, NY (607) 763-3663
- Capital Region Career Technical School, Albany, NY (518) 862-4800
- Career & Technical Institute/ Dutchess BOCES, Poughkeepsie, NY (845) 486-4981
- Dutchess Community College, Poughkeepsie, NY (845) 431-8000
- Erie Community College, Buffalo, NY (716) 842-2770
- Harlem School of Technology, New York, NY (212) 932-2849
- Hudson Valley Community College, Troy, NY (518) 629-4822
- HVAC Career Training, locations statewide (866) 893-0703
- Hvacredu.net (online training) (888) 655-4822
- Isaac Heating and Air Conditioning Inc., Rochester, NY (585) 546-1400
- Mechanics Institute, New York, NY (212) 840-7648
- Mohawk Valley Community College, Utica, NY (315) 792-5400
- Monroe Community College, Rochester, NY (585) 292-2000
- Myers Education Center, Saratoga Springs, NY (518) 581-3600 (HVAC Excellence Accredited Program)
- Suffolk County Community College, Selden, NY (631) 451-4110
- SUNY Delhi, Delhi, NY (607) 746-4070
- SUNY Canton-Camino School of Engineering Technology, Canton, NY (315) 386-7215
- SUNY Erie Community College, Williamsville, NY (716) 851-1155
- Technical Career Institutes, New York, NY (212) 594-4000
- The Refrigeration Institute, New York, NY (212) 244-2588
- The School of Technical Cooperative Education, New York, NY (212) 369-8800

FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the HVAC licensing process in New York State:
Is HVAC a good career in New York?
Yes. Several factors make a career in HVAC a good idea in New York:
- High demand – HVAC systems are essential for residential, industrial, and commercial properties. Skilled technicians are needed to install, repair, and maintain these systems. New York experiences climate and weather fluctuations that make HVAC relevant all year round, and the state’s large population means there is a lot of work to go around.
- Stability – a career in HVAC offers job security and stability, as people will continue to need HVAC systems regardless of economic conditions or recession.
- Career growth – HVAC offers opportunities to advance in your career. You can eventually open your own HVAC business or even start a franchise. As systems become more advanced and require updating, the need for HVAC technicians with updated skills such as internet-connected HVAC devices or energy-efficient approaches will rise.
- Competitive salary – HVAC professionals in New York can earn competitive salaries. While factors like experience, specializations, certifications, and location can impact an HVAC technician’s earning potential, it is considered a well-paying field.
How long does it take to become a certified HVAC technician in New York?
That depends on the educational program and on-the-job training you choose. An HVAC program at a community college or technical school can range from 6 months to 2 years. Apprenticeship programs in which you gain skills and experience under an HVAC technician can last 3-5 years. Licensing and certification, while not required in all parts of New York, can greatly enhance your knowledge and abilities.
Research the various accredited programs and training opportunities to develop a plan for your personal career path as an HVAC technician.
Can I transfer my HVAC certification from another state to New York?
You can, but you’ll need to look into the specific requirements, depending on your existing certification. Some states have a reciprocity agreement with other states, which can streamline the process. Unfortunately, New York State does not have reciprocity with any other state.
Contact the New York State Department of Labor to begin the process of transferring your certification. You’ll likely have to submit an application that includes proof of your current certification, educational transcripts, work experience, and any other supporting documentation. Pay any necessary exam or certification fees and work to meet the additional requirements.
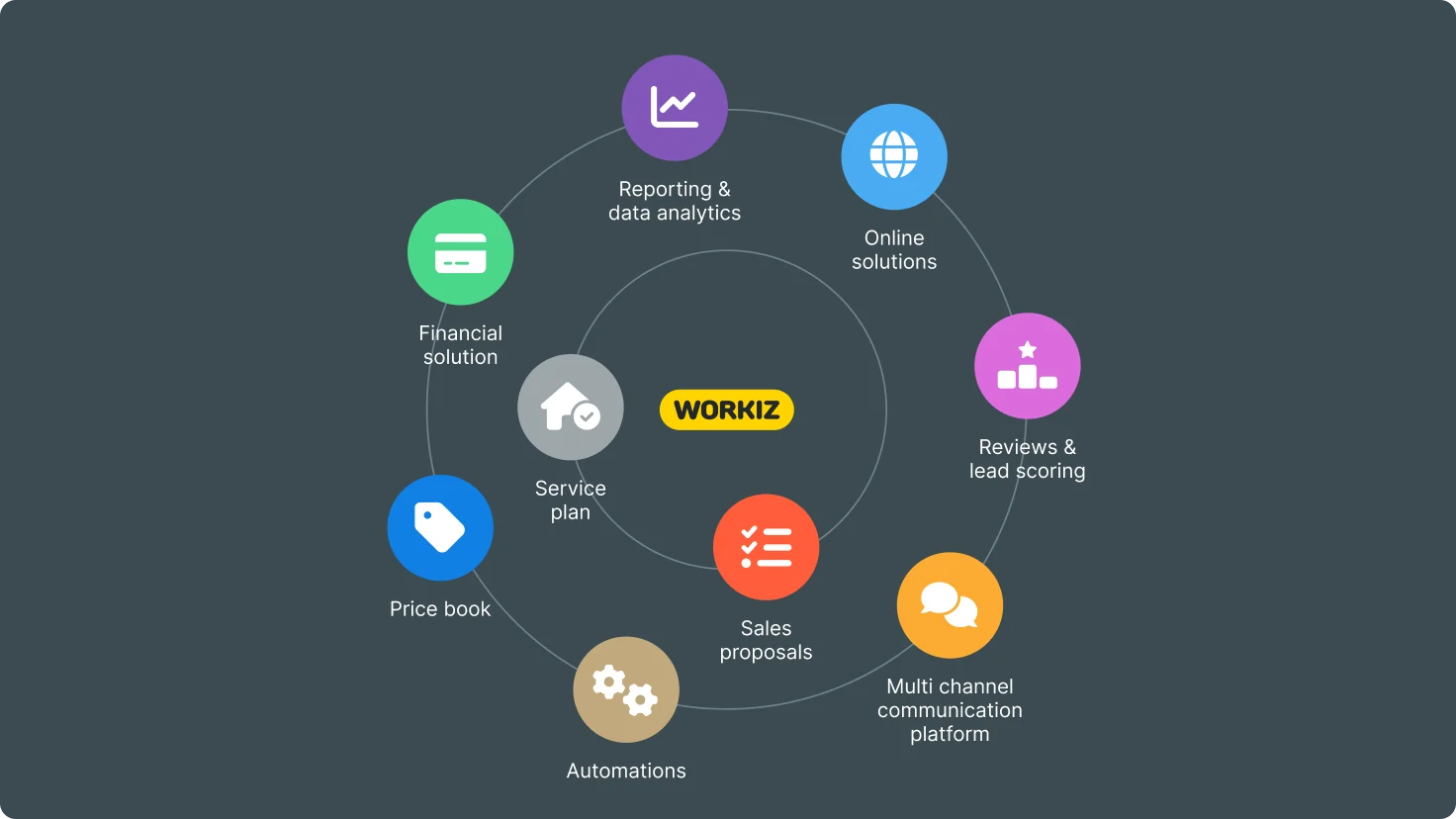
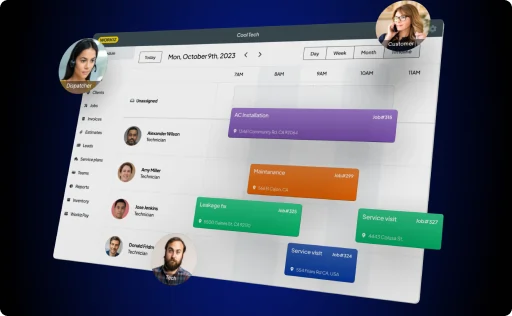
What are useful tools to use in my HVAC business?
As an HVAC professional, you’ll want a tailored tool that is easy to use while helping you maximize your business. Choose a tool that offers the following features:
- Job management capabilities so you can schedule appointments, assign tasks, and track job progress in an efficient manner.
- Payment management so you can send customers professional invoices and process payments digitally.
- GPS tracking so you can effectively optimize your routes.
- Communication tools to send customers seasonal reminders, upcoming appointment reminders, prompts for reviews, and more.
- Database tools to keep track of your customers and personalize your interactions with them for better service and greater satisfaction.
- Analytics tools to identify key metrics, such as job completion rates, customer feedback, ad spend, and more.
- Integration with other business tools such as QuickBooks, Sunbit payment plans, Google Calendar, Mailchimp, and more.
A field management software tool like Workiz offers all of the above, along with many more useful features, making it ideal for both new and seasoned HVAC professionals.